Accurate Diagnosis of Pes Anserine Pain: Key Tests You Must Know!
To go along with today's episode I have a nice infographic to share...
Sign up to receive FREE: PES ANSERINE Pain Evidence Based "Cheat Sheet"
Click HERE to Download FREE
Grab the rest of the Mini Course and Sign up for the Certification Pre-sale list:
- FPF Mini Course - 7 Reasons Why Injuries Happen in the Gym and What to do About it
- The Fitness Pain Free Certification
In today's video we go over Accurate Diagnosis of Pes Anserine Pain: Key Tests You Must Know!
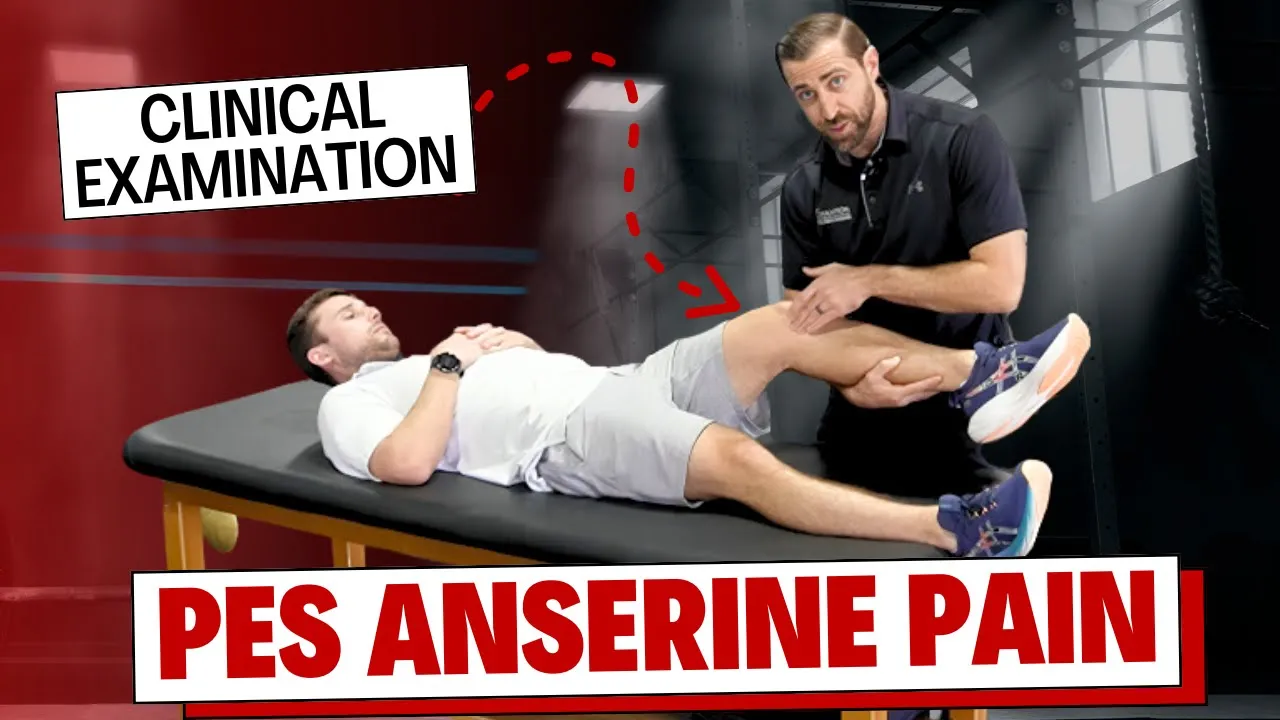
Are you struggling with diagnosing of pes anserine pain in your patients? In this video, I'll guide you through the clinical examination process for pes anserine pain, also known as "the goose foot." This condition often presents unique symptoms and challenges, but with the right approach, you can accurately diagnose and effectively manage it.
Key Takeaways:
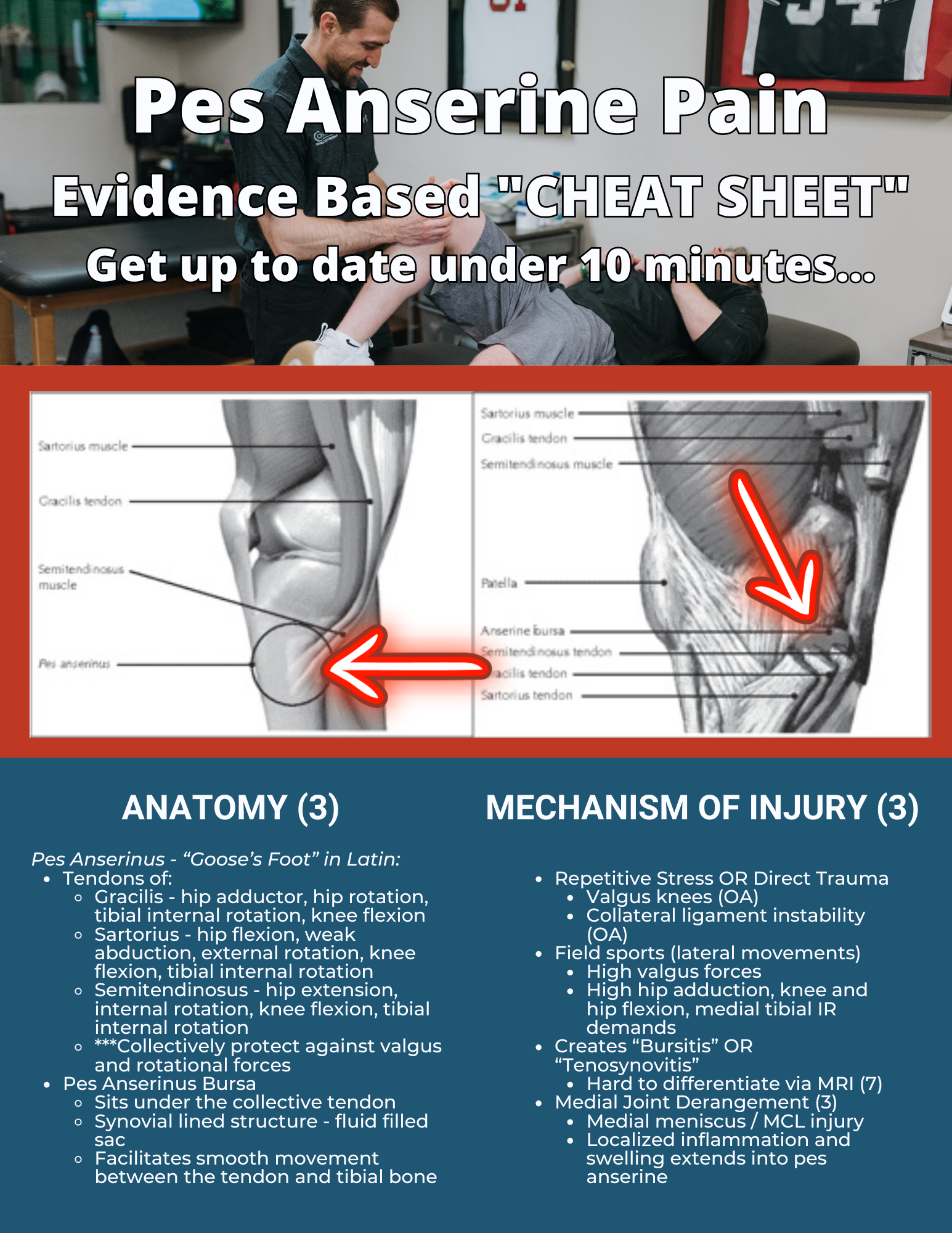
➡️ Definition of pes anserine pain. It's located on the front and medial side of the knee. It’s more common in women over 40, patients with knee osteoarthritis, valgus knee issues, or knee instability, such as MCL insufficiency.
➡️ Examine the anatomy. The pes anserine involves the gracilis, sartorius, and semitendinosus muscles, which converge to reduce valgus forces at the knee. It's common in athletes engaged in sports requiring cutting and pivoting movements.
➡️ Diagnostic steps: Identify pain during step-down tasks, perform hamstring length tests, stretch adductors, and conduct manual muscle testing for knee flexors and adductors to provoke symptoms.
➡️ Differential diagnosis: Identify pes anserine pain and differentiate from from meniscus pathology, osteoarthritis, or MCL injuries by focusing on symptom location and testing joint line tenderness, passive range of motion, and valgus stress.
Learn how to accurately diagnose and manage pes anserine pain in your patients. Watch now to upgrade your skills and help your patients recover faster!
TIMELINE
- 00:00 - Intro
- 00:23 - Pes anserine pain overview
- 00:39 - Common populations
- 02:01 - Symptom location
- 02:50 - Diagnostic steps
- 04:47 - Differential diagnosis
Diagnosis Verified,
- Dan Pope DPT,OCS,CSCS
Show Notes / Relevant Articles:
- FPF Mini Course - 7 Reasons Why Injuries Happen in the Gym and What to do About it
- How to DIAGNOSE IT Band Pain FAST
- Pes Anserine Pain - What Physical Therapists Should Know
- IT Band Pain - Evidence Based Guide [For Physical Therapists]
- IT Band PAIN - 3 Keys to Physical Therapy Treatment
- What Physical Therapists Need to Know [Patellofemoral Pain]
- PATELLAR Tendinopathy Evidence Based Guide [What Physical Therapists Need to Know]
Want to support me and decide topics for future episodes? Click HERE to sign up for FPF "Insiders" for just a dollar. You'll gain access to 100+ webinars, e-books and complete guides. Plus, you'll get private access to the "Insiders" Facebook group where you can have all of your questions answered by me.
Looking for other ways to support me that are 100% free?
- Like, comment and share on youtube, facebook and instagram
- Leave a 5-star review on apple podcasts
Thank you!
Dan Pope DPT, OCS, CSCS
References:
- Pes Anserinus Tendons. Image shows the distance between the insertion of the pes anserinus and the knee joint, which should be considered in the physical examination. Helfenstein Jr M, Kuromoto J. Anserine syndrome [in Portuguese]. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2010;50(3):313-327.
Medial View of the Knee. The image shows the relationship between the tendons that form the pes anserinus and the anserine bursa, implying a difficult clinical and imaging diagnosis. Helfenstein Jr M, Kuromoto J. Anserine syndrome [in Portuguese]. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2010;50(3):313-327.
Mohseni M, Mabrouk A, Li DD, et al. Pes Anserine Bursitis. [Updated 2024 Jan 29]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532941/
Pes Anserine Bursitis Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC. This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
Alvarez-Nemegyei J. Risk factors for pes anserinus tendinitis/bursitis syndrome: a case control study. J Clin Rheumatol. 2007 Apr;13(2):63-5. doi: 10.1097/01.rhu.0000262082.84624.37. PMID: 17414530.
Helfenstein M Jr, Kuromoto J. Anserine syndrome. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2010 May-Jun;50(3):313-27. English, Portuguese. PMID: 21125167.
Rennie, W. J., & Saifuddin, A. (2005). Pes anserine bursitis: incidence in symptomatic knees and clinical presentation. Skeletal Radiology, 34(7), 395–398. doi:10.1007/s00256-005-0918-7
Safran MR, Fu FH. Uncommon causes of knee pain in the athlete. Orthop Clin North Am 1995; 26:547–549
Atici A, Bahadir Ulger FE, Akpinar P, Illeez OG, Geler Kulcu D, Unlu Ozkan F, Aktas I. Poor Accuracy of Clinical Diagnosis in Pes Anserine Tendinitis Bursitis Syndrome. Indian J Orthop. 2022 Jan;56(1):116-124.
Khosrawi S, Taheri P, Ketabi M. Investigating the Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Reducing Chronic Pain in Patients with Pes Anserine Bursitis: A Randomized, Clinical- Controlled Trial. Adv Biomed Res. 2017 Jun 6;6:70. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.190999. PMID: 28626745; PMCID: PMC5468784.
Yoon HS, Kim SE, Suh YR, Seo YI, Kim HA. Correlation between ultrasonographic findings and the response to corticosteroid injection in pes anserinus tendinobursitis syndrome in knee osteoarthritis patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2005 Feb;20(1):109-12. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.1.109. PMID: 15716614; PMCID: PMC2808555.
Finnoff JT, Nutz DJ, Henning PT, Hollman JH, Smith J. Accuracy of ultrasound-guided versus unguided pes anserinus bursa injections. PM R. 2010 Aug;2(8):732-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2010.03.014. Epub 2010 Jul 3. PMID: 20598959.
Sarifakioglu B, Afsar SI, Yalbuzdag SA, Ustaömer K, Bayramoğlu M. Comparison of the efficacy of physical therapy and corticosteroid injection in the treatment of pes anserine tendino-bursitis. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016 Jul;28(7):1993-7. doi: 10.1589/jpts.28.1993. Epub 2016 Jul 29. PMID: 27512249; PMCID: PMC4968491.
Babaei-Ghazani A, Eftekharsadat B, Soleymanzadeh H, ZoghAli M. Ultrasound-Guided Pes Anserine Bursitis Injection Choices: Prolotherapy or Oxygen-Ozone or Corticosteroid: A Randomized Multicenter Clinical Trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2024 Apr 1;103(4):310-317. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000002343. Epub 2023 Oct 2. PMID: 37752656.
Homayouni K, Foruzi S, Kalhori F. Effects of kinesiotaping versus non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and physical therapy for treatment of pes anserinus tendino-bursitis: A randomized comparative clinical trial. Phys Sportsmed. 2016 Sep;44(3):252-6. doi: 10.1080/00913847.2016.1199251. Epub 2016 Jun 22. PMID: 27276165.
Saggini R, Di Stefano A, Dodaj I, Scarcello L, Bellomo RG. Pes Anserine Bursitis in Symptomatic Osteoarthritis Patients: A Mesotherapy Treatment Study. J Altern Complement Med. 2015 Aug;21(8):480-4. doi: 10.1089/acm.2015.0007. Epub 2015 Jun 17. PMID: 26083769; PMCID: PMC4522948.
Gouda W, Abbas AS, Abdel-Aziz TM, Shoaeir MZ, Ahmed W, Moshrif A, Mosallam A, Kamal M. Comparing the Efficacy of Local Corticosteroid Injection, Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy in the Treatment of Pes Anserine Bursitis: A Prospective, Randomized, Comparative Study. Adv Orthop. 2023 Sep 30;2023:5545520. doi: 10.1155/2023/5545520. PMID: 37810418; PMCID: PMC10560108.
Allen MF, Allen DE. Pes Anserinus Bursitis: A Case Report. Cureus. 2022 Nov 11;14(11):e31354. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31354. PMID: 36415475; PMCID: PMC9674038.